How to Choose Models and Specifications for RCCB,Rcd breaker (Household Leakage Circuit Breakers)? Don’t Make the Wrong Choice with Complicated Parameters
In today’s modern household living, electricity has become an indispensable part of our daily lives. However, with the increasing prevalence of electrical equipment, the importance of electrical safety has also grown. To effectively protect our homes, residual current devices, also known as residual current circuit breakers, have emerged. But how do we navigate the wide range of models and specifications? This article aims to provide a detailed analysis of selecting residual current circuit breakers, ensuring a clear understanding and informed decision-making process.

I. Understanding the Basics and Functions of Residual Current Circuit Breakers
1.1 Definition of Residual Current Circuit Breakers
Residual current circuit breakers, also referred to as residual current devices or ground fault circuit interrupters, are protective devices that automatically disconnect the power supply when a leakage current occurs in the circuit, based on the principle of current balance.
1.2 Functions of Residual Current Circuit Breakers:
The primary function of residual current circuit breakers is to protect personal safety, prevent electrical fires, and ensure the normal operation of household electrical equipment.
II. Classifying and Identifying Features of Residual Current Circuit Breakers
2.1 Classification by Application:
Residual current circuit breakers can be categorized into two main types: household and industrial. Household residual current circuit breakers are commonly used in residential and office settings, while industrial residual current circuit breakers are prevalent in production enterprises and engineering projects.
2.2 Classification by Poles:
Residual current circuit breakers can be further classified as single-pole, two-pole, three-pole, or four-pole types. Single-pole and two-pole options are suitable for single-phase circuits, whereas three-pole and four-pole options are ideal for three-phase circuits.
2.3 Classification by Leakage Operating Current:
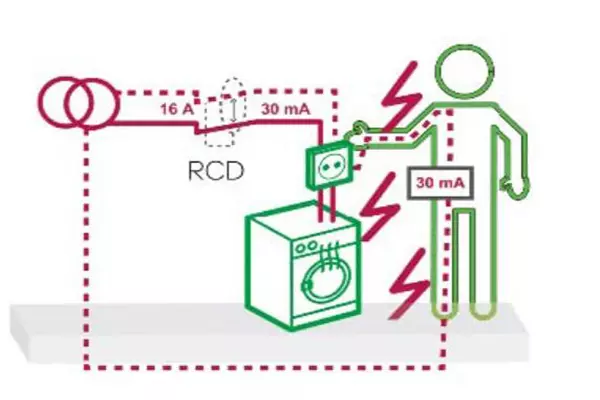
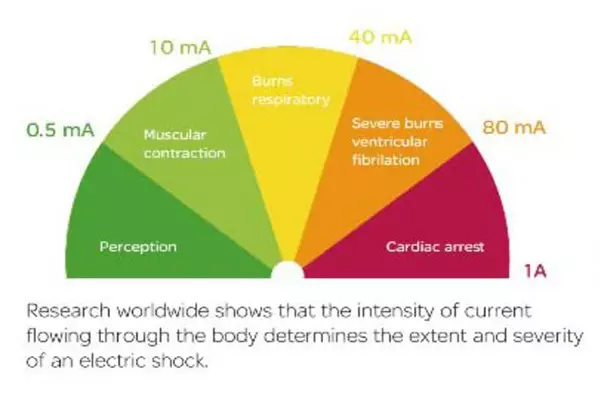
Leakage operating currents vary, typically ranging from 10mA to 500mA. Smaller leakage operating currents provide stronger protection for individuals. For household use, it is generally recommended to opt for a 30mA residual current circuit breaker.

III. Considerations for Purchasing Residual Current Circuit Breakers
3.1 Choosing the Right Brand:
Prioritize products from reputable brands with reliable after-sales service to ensure safety and avoid substandard options.
3.2 Determining the Type of Household Electrical System:
Identify whether your household electrical system is single-phase or three-phase. For single-phase circuits, single-pole or two-pole residual current circuit breakers are recommended. For three-phase circuits, consider three-pole or four-pole options.
3.3 Selecting the Appropriate Leakage Operating Current:
Choose the leakage operating current based on the electrical environment and device characteristics at home. For household use, a 30mA residual current circuit breaker is typically recommended. Adjust the leakage operating current accordingly if special appliances, such as bathing equipment or medical devices, are present.
3.4 Ensuring the Appropriate Rated Current and Voltage:
Match the rated current and voltage of the residual current circuit breaker with the household electrical load. Generally, for household use, the rated current options are 40A, 63A, or 100A, while the rated voltage is 220V for single-phase or 380V for three-phase systems.
3.5 Verifying Product Quality and Certification:
Pay attention to quality markings, safety certifications, and other product information to ensure reliability.

IV. Installation and Usage Guidelines for Residual Current Circuit Breakers
4.1 Suitable Installation Environment:
Residual current circuit breakers should be installed in dry and well-ventilated environments, away from direct sunlight and protected against rainwater intrusion.
4.2 Recommended Installation Height:
The optimal installation height for residual current circuit breakers is between 1.2 meters and 1.5 meters above the ground. This height facilitates convenient operation and observation.
4.3 Installation Methods:
Residual current circuit breakers can be installed either recessed (concealed) or surface-mounted. Recessed installation involves placing the circuit breaker inside the wall, resulting in a neat appearance. Surface-mounted installation, on the other hand, entails installing the circuit breaker on the wall’s exterior, providing easier access for inspection and maintenance purposes.
4.4 Regular Inspection and Maintenance:
To ensure the uninterrupted functionality of residual current circuit breakers, it is recommended to conduct inspections and perform maintenance every six months. This practice helps identify and promptly resolve any potential issues.

V. Common Problems and Solutions
5.1 Frequent Tripping of the Residual Current Circuit Breaker:
If the residual current circuit breaker frequently trips, it may be due to a low leakage operating current setting or the presence of leakage in household appliances. In such cases, it is advisable to check for any leakage issues in appliances and adjust the circuit breaker’s leakage operating current accordingly.
5.2 Inability to Reset the Residual Current Circuit Breaker:
If the residual current circuit breaker cannot be reset, it could indicate continuous leakage in the circuit or a fault within the circuit breaker itself. It is advised to first examine household appliances and circuits for any leakage problems. If the issue persists, consider replacing the faulty residual current circuit breaker.
5.3 Presence of Electric Shock Risk Despite the Residual Current Circuit Breaker:
While residual current circuit breakers play a vital role in personal safety, they do not completely eliminate the risk of electric shock. It remains crucial to exercise caution and take precautions against electric shock when using electrical appliances. This includes avoiding operating appliances in damp environments and refraining from unauthorized wiring.
Conclusion:
The selection and proper usage of residual current circuit breakers are of utmost importance in ensuring household electrical safety. This comprehensive article has provided a detailed guide on the basic concepts, classification features, considerations for purchasing, installation, and usage of residual current circuit breakers. By following the insights presented here, readers can make informed choices and effectively utilize residual current circuit breakers, thereby ensuring electrical safety in their homes and enhancing their quality of life.



